 +86-755-28062190
SetHome
AddFavorite
Welcome to Sanye Technology Co., LTD. official website!
+86-755-28062190
SetHome
AddFavorite
Welcome to Sanye Technology Co., LTD. official website!
CONTACT US
- Address
- 3rd Floor, Building 8-2, Kukeng Tongfu Industrial Zone, Guanlan Street, Longhua District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province
- Phone
- +86-755-28062190 / 13728860027
- wangym@sayestech.com
Water Cooling Is Also Called Liquid Cooling. The Principle Of Water-Cooling Heat Dissipation Is Very Simple: In A Closed Liquid Circulation Device, The Power Generated By The Pump Drives The Liquid Circulation In The Closed System, And The Heat Generated By The Chip Absorbed By The Heat Sink Is Brought To A Larger Area Through The Circulation Of The Liquid. Heat Dissipation Device To Dissipate Heat. The Cooled Liquid Flows Back To The Heat-Absorbing Device Again, And The Cycle Repeats.

Classification Of Water-Cooling Heat Dissipation Systems:
According To The Different Heat Exchange Methods Of The Secondary Heat Exchanger, Water-Cooling Heat Dissipation Systems Can Generally Be Divided Into The Following Three Types: Air Cooling Systems, Liquid Cooling Systems, And Chiller Cooling Systems.
The Air Cooling System Generally Consists Of: Water Cooling Plate, Water Pump, Water Tank, Heat Exchanger And Fan. The System Has A Simple Structure And Is The Most Economical Water Cooling System.
Chiller Cooling System: It Is Composed Of Compressor, Water Cooling Plate, Cooling Tower And Other Parts. In This Way, The Water Temperature Can Be Accurately Controlled Below The Ambient Temperature And The Cooling Capacity Is Large.
The Following Is The Working Principle Diagram Of The Water-Cooled Chiller
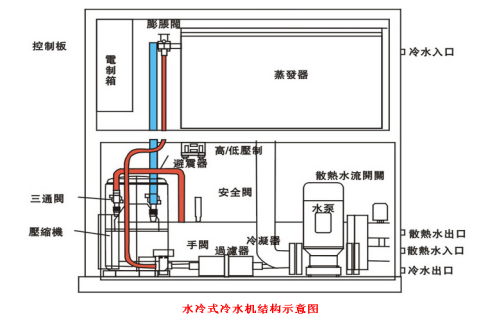
Liquid Cooling System: It Does Not Contain A Compressor And Is Mainly Composed Of A Liquid Exchanger, Water Pump, Water Tank, Etc. It Has Low Noise And Is More Than Half Smaller Than The Chiller.
Selection And Calculation Of Water Cooling Plate:
As An Important Part Of The Water Cooling System, The Cold Plate Mainly Exchanges The Heat Generated By The Heating Components With The Coolant. In Order To Ensure That The Heating Surface Of The Device Can Take Away As Much Heat As Possible When It Is Cooled By The Liquid, The Contact Between The Device And The Cold Plate And The Thermal Resistance Of The Cold Plate Are Particularly Important!To Design A Proper Cold Plate, The Following Parameters Need To Be Determined: Cooling Liquid Flow Rate, Cooling Liquid Inlet Temperature, Heat Dissipation Power Of The Heating Device Installed On The Cold Plate, And The Maximum Allowable Temperature Tmax On The Cold Plate Surface. Knowing These Parameters, You Can Determine The Maximum Allowable Thermal Resistance Of The Cold Plate And Verify It Through Thermal Simulation Analysis.
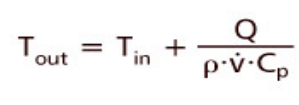
Tout: Cooling Liquid Outlet Temperature
Tin: Cooling Liquid Inlet Temperature
Q: Total Heat Dissipation Power Of The Heating Device On The Cold Plate
Ρ: Density Of The Liquid
V: Cooling Liquid Flow Rate
CP: Specific Heat Capacity Of The Cooling Liquid
Calculate The Maximum Cooling Liquid Outlet Temperature Tout. This Is Very Important. If Tout Is Greater Than Tmax, Then The Cold Plate Will Not Be Able To Solve The Heating Problem.
Assuming That Tout Is Less Than Tmax, The Next Step Is To Determine The Normalized Thermal Resistance Of The Cold Plate ( ), Using The Following Equation:
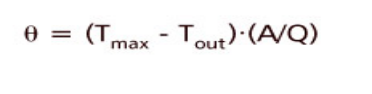
: Thermal Resistance
Tmax: The Maximum Temperature Allowed On The Cold Plate Surface
Tout: Cooling Liquid Outlet Temperature
A: The Area Of The Cooled Area
Q: The Total Heat Dissipation Power Of The Heating Device On The Cold Plate
Design Of Other Parts Of The System:
The Piping System And Valves Are Water-Cooled Systems Important Components Of Hardware Include Quick Connectors, Pipes, Various Functional Valves (Flow Control Valves), Filters, Other Pipe Joints And Seals, Etc.
The Size Of The Pipe (Such As Diameter, Length, Etc.) Should Be Determined According To The Flow Rate Of The Coolant:
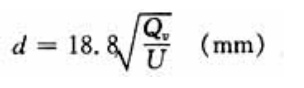
Where Qv Is The Water Flow Rate (M3/H); U Is The Water Flow Rate (M/S). The Diameter Of The Pipe Can Be Calculated. The Pipe Materials Of The System, Taking Into Account The Special Requirements Of The Cooling Medium, Are All Made Of Seamless Stainless Steel Pipes And Partially Made Of Polyurethane Pipes.
Coolant: The Heat Transfer Capacity, Freezing Point And Viscosity, Boiling Point And Decomposition Temperature, Insulation Properties, Corrosiveness, Flammability, Toxicity, Cost, Etc. Of The Coolant Must Be Considered. Commonly Used Coolants Include Water, Ethylene Glycol Solution, Silicone Oil, Etc.
Pump
The Pump Is The Main Part Of The Cooling System And Its Purpose Is To Circulate The Coolant At The Flow Rate Required To Overcome The Total Fluid Friction Heat In The Cooling Circuit. Commonly Used Pumps In Cooling Systems Include Centrifugal Pumps, Vortex Pumps And Gear Pumps.
The Selection Of The Pump Is Mainly Determined Based On The Flow Rate Qv And Pressure Head H Required By The Cooling System. In Order To Facilitate Adjustment, Usually The Total Lift Of The Water Pump Should Be Approximately 15% To 20% Greater Than The Calculated Pressure Of The Cooling System, And The Flow Rate Should Be Approximately 15% To 20% Greater Than The Calculated Value.
-
Phone
+86-755-28062190 -
Wechat



 CN
CN